The elderly population is rapidly rising. In 1950, there were 205 million people aged 60 years or over, while in 2000 there were 606 million. By 2050, the global population aged 60 or over is projected to expand by more than three times its current level; reaching nearly 2 billion people. Of these, the number of people aged 80 years or more is set to almost quadruple to 395 million between now and 2050.
This is incredible, especially when in 1910 the life expectancy of a Chilean female was 33 years. Today, it is 82 years, and this increase is similar for most nationalities. This represents a remarkable gain of almost 50 additional years in one century, which is largely due to public health improvements. However, many leading scientists are predicting the best is yet to come.
The May 2013 issue of the National Geographic Magazine carried a picture of a baby on its cover with the headline: “This Baby Will Live To Be 120” with the title “It’s not hype, new science could lead to very long lives.” Obviously though, quality of life is just as important when it comes to longevity.
Harvard geneticist, David Sinclair’s work is widely documented. In 2006, he led a team of Harvard Scientists to discover “resveratrol” reversed the aging process in cells. Resveratrol (250 times more effective when taken by intraoral spray) is a natural occurring compound that enhances mitochondria, the cell’s energy factories that lead to a more efficient metabolism and the body having less toxic waste.
Sinclair reports ‘There are now a number of compounds being tested in the lab that greatly slow down the aging process and delay the onset of diabetes, cancer and heart disease.”
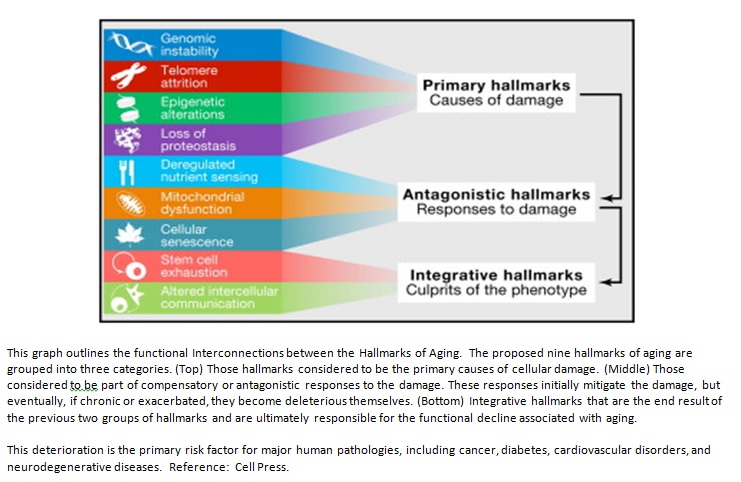
Aging is a process characterized by progressive functional decrease of all organs, morphological changes, and immune system-related changes at the cellular and molecular levels, which determine less adaptive biologic functions. The immune system alternations in the elderly are comprehensively known as immunosenescence. Immunosenescence refers to the gradual deterioration of the immune system. This phenomenon is characterized by an accumulation of changes that progressively result in dysfunctional or compromised immune responses. Having a healthy and strong immune system is vital throughout one’s entire life time. A weak immune system provides an opening for viruses, fungi and parasites to take hold, which can then lead to cancer. The immune system is extremely important as it protects the body against infection. It is a fact that cancer-related mortality increases with age: 70% of all malignancy-related deaths are registered in people aged 65 or older.
Multiple aspects of aging are involved that include: thymic involution (which is the shrinking of the thymus with age), shifts in the number, distribution and activity of T- and B- lymphocytes, reduced availability of CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells, impaired production of naïve B-cells in the bone marrow, dysfunction of antigen presenting cells (APCs), alterations of cytokines production, frequent immunoglobulin production, skewing of B cell production that are more likely to generate auto-antibodies. Inflammation has also been shown to be a promoter of cellular senescence (which is the phenomenon when cells lose their ability to divide or replicate and they reach what is known as their Hayflick limit).
Environmental modifications (e.g. increments of oxygen concentration and free oxygen radicals, DNA damage), and stress can also induce the aging process. In addition, telomeres shorten with age and stem cell regeneration and release rates decline.
To see more about the nine cycles of aging please click this link to an earlier blog.
http://www.stemcellworx.com/blog/prevent-aging-with-cell-health
Advanced science and technologies are enabling incredible breakthroughs to occur, especially in the field of gene therapy and stem cells. These major advancements are being supported by a multitude of recently published clinical trials and research papers.
This is why adult stem cell abilities are so incredible. Adult stem cells are undifferentiated cells, found throughout the body after development, that multiply by cell division to replenish dying cells and regenerate damaged tissues. Adult stem cells are found in juvenile as well as adult animals and human bodies.
Scientific interest in adult stem cells is centered on their ability to divide or self-renew indefinitely, and generate all the cell types of the organ from which they originate, potentially regenerating the entire organ from a few cells. Unlike embryonic stem cells, the use of human adult stem cells in research and therapy is not considered to be controversial, as adult stem cells are derived from adult tissue and reside in one’s body after we are born, rather than having to come from a human embryo.
A recent paper published by the journal Cell Stem Cell reported human stem cells (HSC) residing in the end (trabecular region) of the bones display the highest regenerative ability of the blood and immune system. “Like the best professional hockey players, our findings indicate blood stem cells are not all equal,” said Bhatia. Bhatia, who also holds a Canada Research Chair in Human Stem Cell Biology, said that cells surrounding the best blood stem cells are critically important, as these “stem cell neighbors” at the end of the bone provide the unique instructions that give these human blood stem cells their superior regenerative abilities.
It is only now that these findings have been validated even though bone marrow transplants have been done for more than 50 years and are routine in most hospitals, providing a life-saving treatment for cancer and other diseases including leukemia, anemia, and immune disorders.
There is no doubt about it. With so many advanced anti-aging, biological and scientific developments on the horizon we are living in very exciting times. Keeping our own adult stem cells active and healthy is vital. Stem Cell Worx Intraoral Spray is at the forefront of stem cell nutrition with its high grade, pure ingredients (including a 98% pure trans-resveratrol) and its intraoral spray delivery provides maximum absorption.
Watch the video below to hear about latest findings on how resveratrol helps prohibit tumor cells.
Resources:
June 9, 2014 – Source: Mount Sinai Medical Center
August 1, 2013 – Source: McMaster University
Immunity & Ageing 2012, 9:4 doi:10.1186/1742-4933-9-4.